Figure 10: Functions of Positive and Negative Tetrahedra in Tensegrity Stacked Cubes
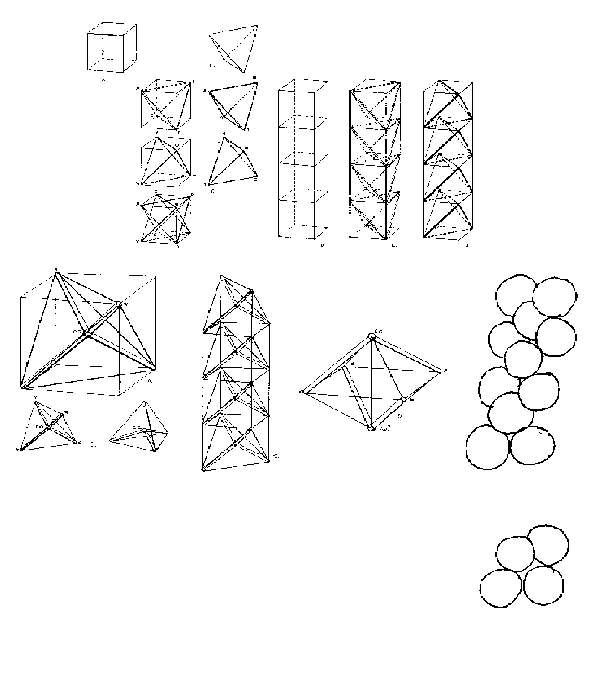
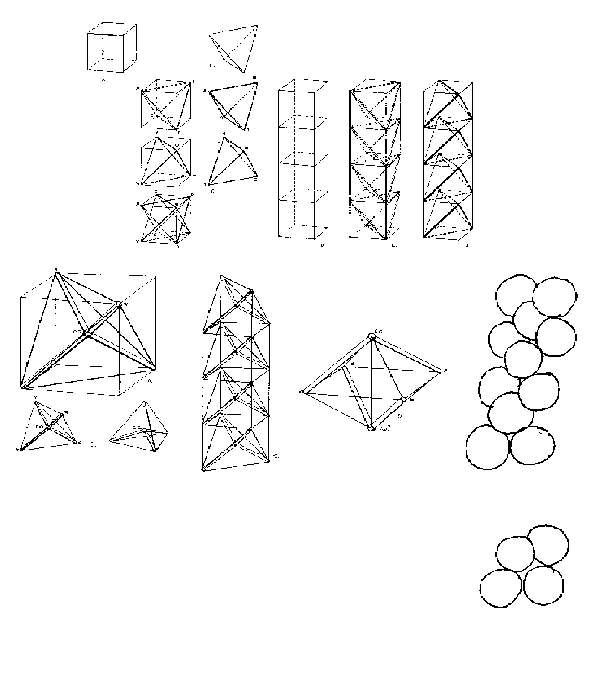
Stabilization of Tension in Tensegrity Column: We put a steel sphere at
the center of gravity of a cube which is also the center of gravity of tetrahedron and
then run steel tubes from the center of gravity to four comers, W, X, Y, and Z, of nega-
tive tetrahedron (A). Every tetrahedron's center of gravity has four radials from the
center of gravity to the four vertexes of the tetrahedron (B). In the juncture between
the two tetrahedra (D), ball joints at the center of gravity are pulled toward one another
by a vertical tension stay, thus thrusting universally jointed legs outwardly, and their
outward thrust is stably restrained by finite sling closure WXYZ. This system is nonre-
dundant: a basic discontinuous-compression continuous-tension or "tensegrity" struc-
ture. It is possible to have a stack (column) of center-of-gravity radial tube tetrahedra
struts (C) with horizontal (approximate) tension slings and vertical tension guys and di-
agonal tension edges of the four superimposed tetrahedra, which, because of the (ap-
proximate) horizontal slings, cannot come any closer to one another, and, because of
their vertical guys, cannot get any further away from one another, and therefore com-
pose a stable relationships a structure.